PAP SMEAR

Primary Care & Internal Medicine located in Hollywood, FL
Pap smear is used to detect abnormal changes in the cells of your cervix. How often you should get a Pap smear depends on your age, your medical history, and the results of your last Pap smear.
Take care of your health and go to a specialist to verify that you do not present any disease. Remember that cervical cancer treatment will be much more effective if the condition is detected at an early age.
At Texas Health Providers, we will help you with whatever you need, since we have the best specialists who will treat your health problems. If you want to book an appointment, you can do so through our Online Appointments section.
PAP SMEAR
What is a Pap smear?
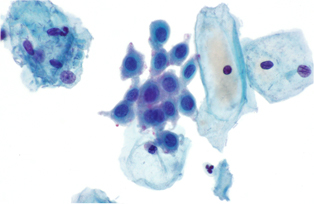
Generally, Pap smear is a screening test to collect and examine under a microscope cells obtained from the cervix, which is the narrow lower part of the uterus located between the bladder and rectum. The cervix forms a canal that opens into the vagina, which is the exit to the outside of the body. In the Pap smear, cells can be taken from both the vagina and the cervix.
For every woman, it is vitally important to know what cervical cancer is, what the Pap test is, what it consists of, and how technology has evolved in women’s health tests.
Cervical cancer is the disordered growth, development and multiplication of the cells of the cervix. It is the second most common cause of death in USA, and this type of cancer is associated with infection by the Human Papilloma Virus, which is transmitted through sexual contact at some point in their lives.
Symptoms
Only one in a thousand women infected with this virus can develop cancer, and some symptoms of cervical cancer are:
- Bleeding between menstrual cycles
- Abnormal vaginal discharge or pain
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Bleeding after menopause
Have you ever wondered at what age it is advisable to perform the first Pap smear? Do you know what this procedure involves?
Why Do You Need a Pap smear?
You should start getting regular Pap smears starting at age 20. How often you should get tested depends on your age, medical history, and the results of your last Pap or HPV test. Usually:
● If you’re between the ages of 20 and 29, get a Pap test every 3 years;
● If you’re between the ages of 30 and 65, get a Pap smear and HPV test every 5 years;
● If you’re older than 65, you may no longer need to have a Pap test.
You may need to be tested more often if you’ve already had a cervical problem, if you have a weak immune system. Our doctors from Texas Health Provider will tell you which tests you need and how often to have them.
What you can expect from a Pap smear?
A Pap smear involves taking cells from the cervix and examining them under a microscope to see if they are normal or abnormal. It is a common and important screening test, as cells from the cervix can tell us about your reproductive health, including showing evidence of cell changes caused by HPV, which can lead to cervical cancer.
Therefore, having a Pap smear from our clinic is an important part for our doctors to maintain good reproductive health for you. But for some people, the concept of a Pap smear can be stressful.
Fortunately, the appointments with our doctors are pretty standard, and knowing what the test will consist of ahead of time can help you feel a little better about knowing what to expect.
Before the Pap smear
You don’t need to do much to prepare for your Pap smear – the most important thing you can bring to our primary care clinic is yourself. However, there are a couple of things to keep in mind when preparing for your date. For starters, if you’re on your period the day of your appointment and your flow is heavy, you may need to call Texas Health Providers’ specialist and make sure it’s okay to test.
Remember that, we can do Pap smears during your menstruation, but heavy discharge could potentially obstruct test results. Additionally, we suggest as your health care provider to refraining from using tampons, having vaginal intercourse, or using any vaginal creams or gels for at least two days before your appointment with our doctors.
During the Pap test
Once you are in the test room, you will undress and our doctor will ask you to lie down on the exam table. Once our doctor is ready, he will ask you to put your feet in stirrups, spread your legs apart, and stay relaxed. Our doctor will insert a speculum into your vagina, which is an instrument that holds the walls of the vagina apart so our doctor can get a better view of the cervix.
If you feel stressed or tense during this part, try squeezing your hands or wiggling your toes; both are useful ways to relieve tension without moving the rest of the body.
The doctor will take some samples of your cervical cells by using a brush or other device to scrape some cells from the cervix, which will only last a few seconds. After that the doctor remove the speculum and may perform a quick hand exam while their hands are still gloved. This part will be very short, and once it’s done, it’s the end of the test!
Keep in mind that none of these steps should hurt, so if you experience any discomfort tell the doctor right away so he can take action and make adjustments to ease the discomfort and help you feel more comfortable.
After the Pap smear
After the test is complete, our doctor will send your cells to our lab to examine, and once the results are ready, we will mail to you within two weeks of the test. You may not receive any information if the results are normal, but if the results are abnormal, we will schedule a follow-up appointment.
Advice for our patients
A Pap smear can be a little uncomfortable, but this test can have a big impact on your health, so it’s worth it. If you have any concerns or experience discomfort, be sure to tell our specialist from Texas Health Providers, who can help you through the process. After treatment, we advice you to follow:
- See your doctor regularly for a Pap test. If the results are abnormal, talk to our doctor.
- Get the HPV vaccine to be protected against the types of HPV that cause cancer of the cervix, vagina, and vulva
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse
- Limit the number of your sexual partners.
Services we Provide
Providers build personal relationships with each patient to help them resolve even the most stubborn health concerns.